ANASYG-PRESYG symbolism
A. Basic elements for the synoptic situation
|
|
| D = D↓ D↑ | Localisation and evolution of the lows. |
| A = A↓ A↑ | Localisation and evolution of the highs. |
| B+ | Situation of the blocking type: high anomaly. |
| B- | Situation of the blocking type: low anomaly. |
| d | Heat lows. |
| δ | Orographic lows. |
| DHugo | Low originating from an ex-tropical cyclone. |
| DP | Polar lows. |
|
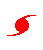
Hurricanes. |
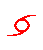
|
Tropical storms. |
|
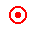
Tropical depressions. |

|
Low level jets. |
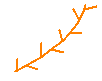
|
Surface or very low levels convergence lines. |
B. Synoptic dynamics markers.
|
|
|
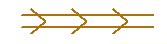
Jet stream, upper troposphere maximum wind axis |
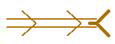
|
Area of strong diffluence at the exit. |
|
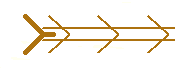
Area of strong confluence at the entrance. |

|
Latent tropopause anomaly. |

|
Dynamic tropopause anomaly. |

|
Upper troposphere trough. |
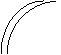
|
Moderate easterly waves (shallow, surface-1500 m). |
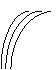
|
Enhanced easterly waves (deep, surface-3000 m). |
C. The bad weather systems.
|
|
The surface fronts, in "frontogenesis"
|
|
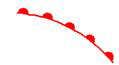
|
Warm front. |

|
Cold front. |
Active occluded fronts
|
|

|
Occlusion. |
Split cold fronts or "Catafronts"
|
|
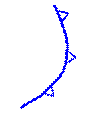
|
A front at upper level (about 600 hPa). |
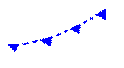
|
Intersection of the front with the surface. |
Frontolysing fronts
|
|
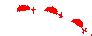
|
Warm front. |
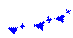
|
Cold front. |
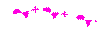
|
Almost stationary front. |
The pseudo-fronts
|
|

|
Pseudo warm front. |
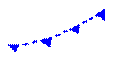
|
Pseudo cold front. |

|
Pseudo almost stationary. |

|
Pseudo subsident front. |
D. Precipitating activity.
|
|
Activity of the fronts.
|
|

|
Weak precipitations. |
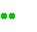
|
Moderate precipitations . |
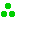
|
Strong precipitations . |
Precipitating areas.
|
|
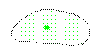
|
Weak. |
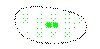
|
Moderate. |
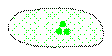
|
Strong. |
E. The areas of strong convection.
|
|
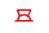
|
Convective activity. |
In cold air.
|
|
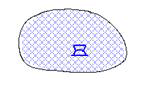
|
Strongly active depression rear. |
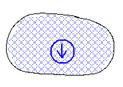
|
Strongly subsident depression rear. |

|
Convection organised in lines. |
In warm air.
|
|
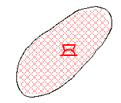
|
Strong convective instability area. |
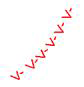
|
Squall lines. |
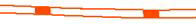
|
Inter Tropical Convective Zone, active ITCZ. |

|
Inter Tropical Convective Zone, ITCZ with no convective activity . |
F. Others.
|
|

|
Sand advection. |